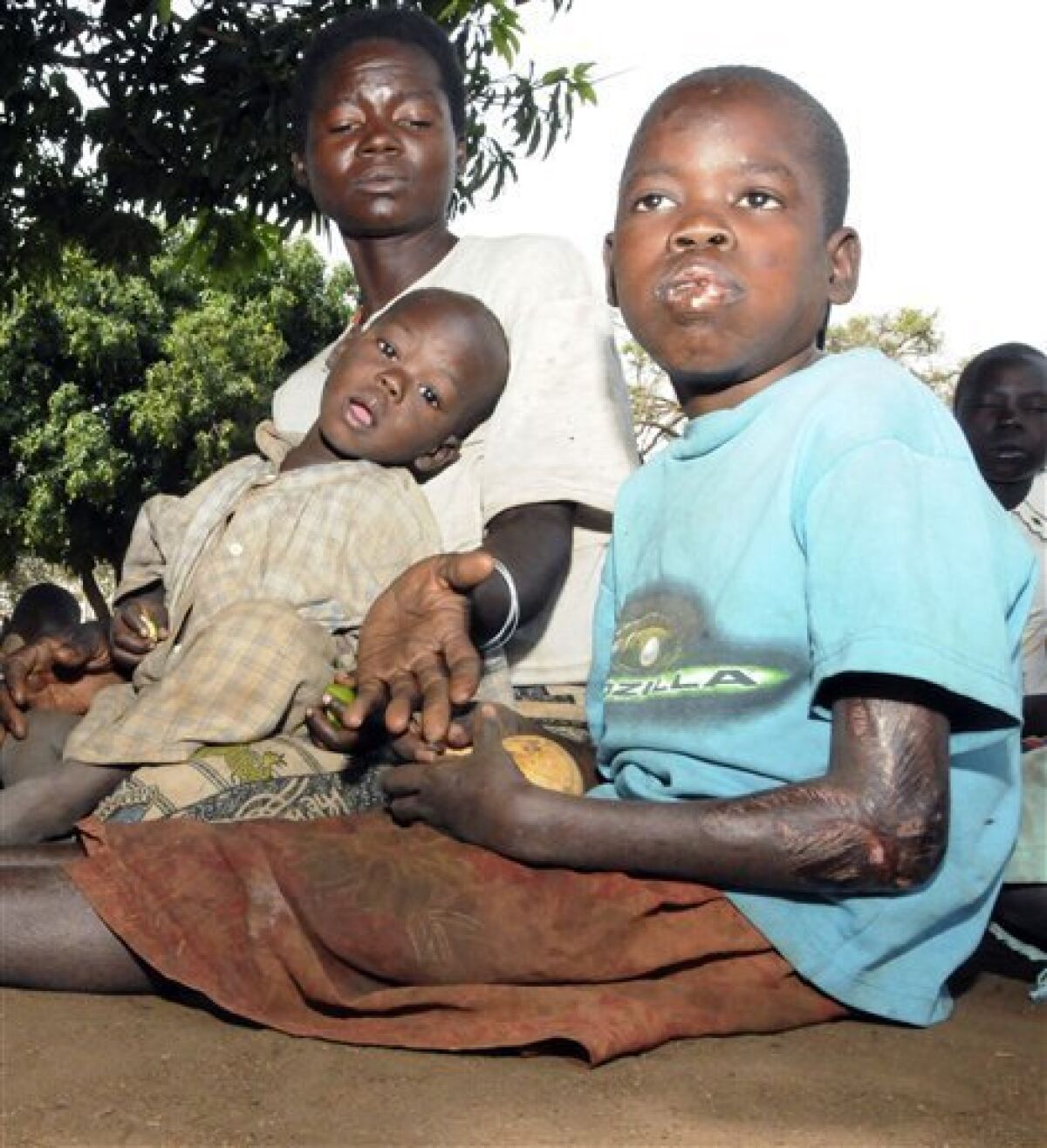
Nodding head syndrome, also known as anoxic nodding syndrome (ANS), is a rare neurological disorder that is typically seen in children and adolescents. It is characterized by recurrent episodes of nodding of the head, which can be accompanied by altered consciousness, seizures, and other neurological symptoms. In recent years, however, cases of nodding head syndrome have been reported in adult patients. If you are looking for the services of charity funds for education, you may go through online sources.
Image Source: Google
Symptoms
The main symptom of nodding head syndrome is recurrent episodes of head nodding, usually lasting between a few seconds and a few minutes. During these episodes, the patient may appear to be in a trance-like state, with decreased responsiveness and awareness. Other symptoms may include confusion, altered consciousness, seizures, memory loss, and difficulty speaking.
Causes
The exact cause of nodding head syndrome is not yet known. However, it is believed that some type of environmental factor may trigger the disorder, such as exposure to a toxin, an infection, or a head injury. Other potential causes include genetic factors, metabolic or nutritional deficiencies, or a combination of these factors.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of nodding head syndrome is typically based on the patient’s medical history, physical examination, and neurological tests. Brain imaging tests, such as an MRI or CT scan, may also be used to rule out other possible causes of the symptoms.
Treatment
There is no specific treatment for nodding head syndrome, but there are measures that can be taken to manage the symptoms. These may include medications to control seizures, physical and occupational therapy, and lifestyle modifications. In some cases, surgery may be recommended to help reduce the severity of the symptoms.